Five years ago I wrote and published a book called The Six Keys to Optimal Health. I really contemplated the concept of adding a seventh key, which would have been hygiene, but I resisted because I made a gross assumption–that pretty much everybody in the modern world is attuned to this paramount health practice.
I now realize that I was severely wrong. In fact, improper hygiene seems to be a continuing scourge of the new millennium. From dirty hospital rooms, leading to an increased spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria, to dirty tattooing equipment, to dirty soda fountains, it’s pretty clear to me that human beings haven’t yet gotten this one down, so let me say it loud and clear: WASH YOUR HANDS!
Whew, I feel better. According to researchers at the Canadian Center for Occupational Health and Safety,
“Hand-washing is the single most effective way to prevent the spread of infections. You can spread certain ‘germs’ (a general term for microbes such as viruses and bacteria) by touching another person even casually. You can also catch germs when you touch contaminated objects or surfaces and then touch your face,” the group explained in a news release from the Society for Women’s Health Research.
Yes, wash people. You go to the WC…wash. You shake somebody’s hand…wash. You handle money…wash. You touch food? Wash. You work with people? Wash. You have kids with snotty noses? Wash dang it!
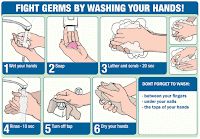
Oh waaait…you don’t know how to properly wash your hands? Got it…okay, well here you go…straight from the Centers of Disease Control:
- Place hands under clean, running water.
- Once wet, add soap and rub hands together until suds form.
- Scrub on every surface for at least 20 seconds (the amount of time it takes to sing “Happy Birthday” twice), including both sides, between fingers and under fingernails.
- Rinse hands again under running water and dry with a clean dry towel or air-dry.
Listen, proper hygiene is so important it’s often the difference between developed nations and third world countries. Some people even believe that it was the improvement in methods and practices of hygiene and not vaccinations that led to the dramatic decrease in death and illness due to infectious microorganisms–I’m one of these people.